FXS- Foreign exchange service
FXS (Foreign Exchange Subscriber) is the port that actually delivers the analog line to the subscriber. In other words, it is the “plug in the wall” that delivers a dial tone, battery current and ring voltage. This is the jack or interface to the phone system which FXO devices can be connected to.
The telecommunication circuit between central offices that implements foreign exchange service has complementary interface types at each end. At the foreign central office that provides the service, the interface is called the foreign exchange office (FXO) end, and at the end where the subscriber station is connected, it provides the foreign exchange station (FXS) interface.
Difference between FXO and FXS ports
FXS (Foreign Exchange Subscriber) is the port that actually delivers the analog line to the subscriber. In other words, it is the “plug in the wall” that delivers a dial tone, battery current and ring voltage. … FXO (Foreign Exchange Office) is the port that receives the analog line.
FXO and FXS are always paired, i.e similar to a male / female plug. If no phone system is used the telephone (FXO) is directly connected to the FXS port. The port is provided by the telephone company.
If you have a PBX, then you connect the lines provided by the telephone company to the PBX and then the phones to the PBX. Therefore, the PBX must have both FXO ports (to connect to the FXS ports provided by the telephone company) and FXS ports (to connect the phone or fax devices). Many traditional phone systems provide both, FXS and FXO ports while many IP Phone systems require additional gateways to provide FXS or FXO ports.
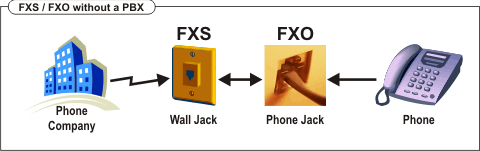
A phone call received via an analog line is initiated like this: Pick up the phone of the FXO device. The FXS port on the corresponding sides recognizes that the call should be established and expects the number, encoded as DTMF signals.
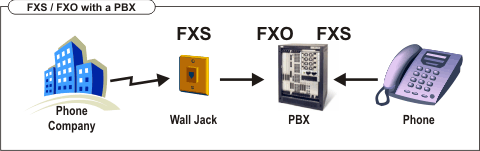
An incoming call works like this: The FXS port provides the necessary electricity. The phone starts ringing. By picking up the phone, the call is established.
FXS/FXO Procedures – How Does it Work in Detail
If you are interested to know in more technical detail how an FXS/FXO port interoperates, here is the exact sequence:
When you wish to place a call:
- You pick up the phone (the FXO device). The FXS port detects that you have gone off-hook.
- You dial the phone number, which is passed as Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) digits to the FXS port.
Inbound call:
- The FXS port receives a call, and then sends a ring voltage to the attached FXO device.
- The phone rings.
- As soon as you pick up the phone you can answer the call.
Ending the call – normally the FXS port relies on either of the connected FXO devices to end the call.
